
Over 2 million + professionals use CFI to learn accounting, financial analysis, modeling and more. Unlock the essentials of corporate finance with our free resources and get an exclusive sneak peek at the first module of each course. Start Free
Sukuk (Islamic bond or “Sharia-compliant” bond) is an Islamic financial certificate that represents a portion of ownership in a portfolio of eligible existing or future assets. They can be considered as an Islamic version of conventional bonds.
Sharia (Islamic law) prohibits lending with interest payments (riba), which is considered usurious and exploitative in nature. Thus, bonds are forbidden in Islamic finance.

Sukuk does not represent a debt obligation. Upon its issuance, the issuer sells certificates to investors. Then, the issuer uses the proceeds from the certificates to purchase the asset, and investors receive partial ownership of the asset. The investors are also entitled to part of the profits generated by the asset.
Sukuk is an alternative to conventional bonds. Islamic and conventional bonds share the following characteristics:
Despite the similarities, there are few important differences between Islamic and conventional bonds, as summarized in the table below:
| Sukuk | Bonds | |
|---|---|---|
| Ownership | Partial ownership of the asset | Debt obligation |
| Compliance | Complies with Sharia | Complies with country/region of issuance |
| Pricing | Based on the value of the underlying asset | Based on issuer's creditworthiness |
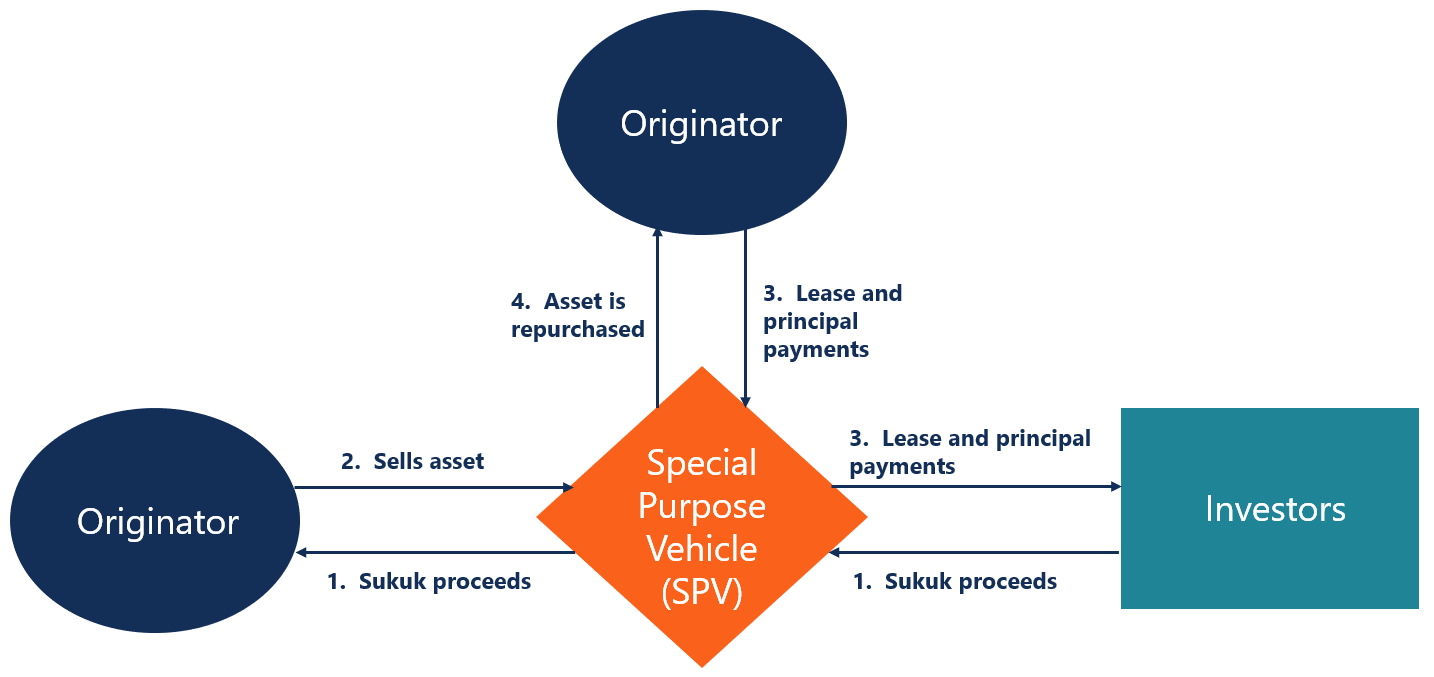
The unique nature of Sukuk requires a specific issuing process for the financial instrument. The following steps are common in the issuance process:
Thank you for reading CFI’s guide on Sukuk. To keep learning and developing your knowledge of financial analysis, we highly recommend the additional resources below:
Get Certified for Capital Markets (CMSA®)From equities, fixed income to derivatives, the CMSA certification bridges the gap from where you are now to where you want to be — a world-class capital markets analyst.